INTERACTIVE PATIENT CASE SCENARIOS FOR UNDERGRADUATE MEDICAL STUDENTS
CLIENTS
The University of Dundee, School of Medicine
Content Creators - Dr. Penny Lockwood, Dr. John F. Dillion
Imaging data and medical contributor - Dr. Richard Oparka
OVERVIEW
The University of Dundee School of Medicine is at the forefront of digital teaching. Students not only get to experience lectures and smaller group sessions but they are also exposed to a whole array of online tutorials and e-learning resources. These resources focus on encouraging students to link basic sciences, such as anatomy, biochemistry and physiology, with the core clinical problems that a patient may present with.
Stand alone Patient Case Scenarios interactives provide a great resource for applying anatomical and pathological learning to ‘real-world’ scenarios. These case studies were written by content experts for undergraduate medical students.
THE CHALLENGE
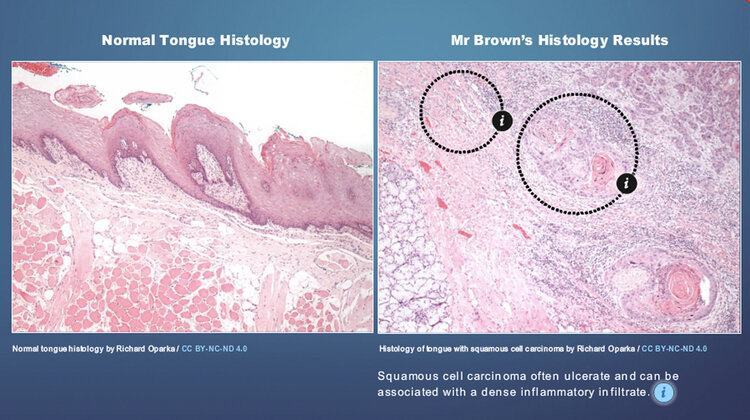
Previous teaching resources for this module relied heavily on histology images and clinical imaging, however they were unlabelled and had very little descriptives to help students understand what they were supposed to be looking for. Furthermore there was not graphical structure to the module, making navigation challenging for the user.
THE SOLUTION
To help with their understanding we worked with Dr. Oparka to provide labelled visual comparisons of normal imagery vs images of when things go wrong. The accompanying text were also elaborated on as well as external links to further information added, should the student wish to read more.
Interactive illustrations were created to help students understand layers upon layers of pertinent anatomy. The illustrations are reused throughout the module to maintain visual continuity. They can also be reused in lecture material and other educational resources.
To connect what the students learn in the classroom with diagnostic visuals, we sourced additional information of the condition that are accompanied by MRI or histology visuals commonly seen as part of the diagnostic and treatment route.